Soil Water Content Management
In order to practice good water management, farmers need to use an irrigation system that enables the plant to grow continuously by making sure it has access to a balanced mix of soil, air, oxygen and nutrients.
By Romeo Dragan – Product Manager Rivulis Irrigation
We would like to delve deeper into the importance of Soil Water Content Management in today’s agriculture and to explain concepts such as Total Available Water (TAW) and Readily Available Water (REW). Monitoring and adjusting the soil water balance according to the crop requirements in different growth stages is a key success factor to achieving desired crop growth and quality.
We first need to review terminology and calculations for Soil Water Content to help us understand the different interaction between plant and Soil Water Balance:
- Total soil moisture: Refers to the total quantity of water that can be found in the soil at any given moment.
- Readily available water: Refers to the quantity of water the plant can access from the soil.
Different levels of Soil Moisture
- Saturation: When we say the soil is saturated with water, it means that the water has occupied all the spaces in between the soil particles and as a result there is no air in the soil. This phenomenon can occur when we irrigate too much or we have too much rainfall and the soil has a low drainage capacity.
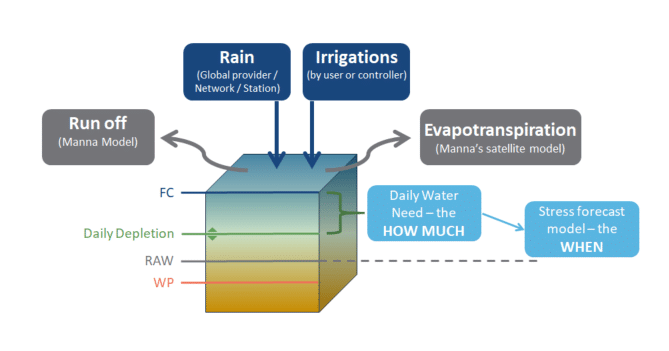
- Field capacity: Refers to the quantity of water which the soil is able to retain once soil drainage has stopped and the water content in the soil has stabilized.
- Wilting point: When the quantity of soil moisture is so low that the plant is no longer able to extract water from the soil. The difference between field capacity water content and the wilting point water content is the Total Available Water, and is affected by the soil type and the root zone depth. In proper Soil Water Balance management in order to provide the optimum growth conditions for the plants, growers keep the level of Soil Moisture in the soil below the saturation point and field capacity but above the wilting point.
Readily Available Water
For optimal plant growth and development, different levels of soil moisture are required throughout the different plant growth stages. The following example is a common requirement for maize/corn:
- Early vegetative stage – The optimum soil humidity is 90-95% of the field capacity. Above 95% of field capacity, we risk soil saturation; roots stop developing and no longer have the capacity to extracts water and nutrients.
- Flowering and pollination –In this stage, the plants’ water consumption reaches its peak. In this stage, the total soil moisture should not drop to 20% or lower than field capacity otherwise yield potential can be reduced.
- Fruit/grain – In this stage, the plant is focused on fruit and grain development and overwatering may cause plants to abort fruit/grain limiting yield potential. Underwatering can cause low sugar content fruits and low tests weight grains.
- Maturation and pre-harvest – Proper moisture management required to maintain fruit and grain quality. For grains, Total Soil Moisture should be maintained at ~40% of Field Capacity. For fruit, Total Soil Moisture should be maintained at ~30% of Field Capacity. Overwatering delays the maturation process and under watering reduces crop yield.
Note: The above example is a general guide only. Of course, consult with an agronomist for your specific crop needs.
Conclusion
In Soil Moisture Content Management, it is important to understand the soil type we are dealing with, the water quality as it is influencing the infiltration rate and the water movement in the soil both vertically and horizontally and the plant’s water requirements.
Farmers have tools available to help them manage the Soil Moisture Content and these tools can range between physical hardware installed in the field to satellite imagery that can detect the plant’s health and development from space. Rivulis has developed Manna Irrigation Intelligence, its satellite-based software solution which makes irrigation decisions simple.Learn more about how Manna Irrigation helps growers know how much and when to irrigate in order to achieve the correct Soil Moisture Content in the soil.
Read more about Soil Considerations for Water Management.