Nutrient Management In Almond Orchard
Nutrient Management for Optimal Almond Production
Understanding Nutrient Dynamics
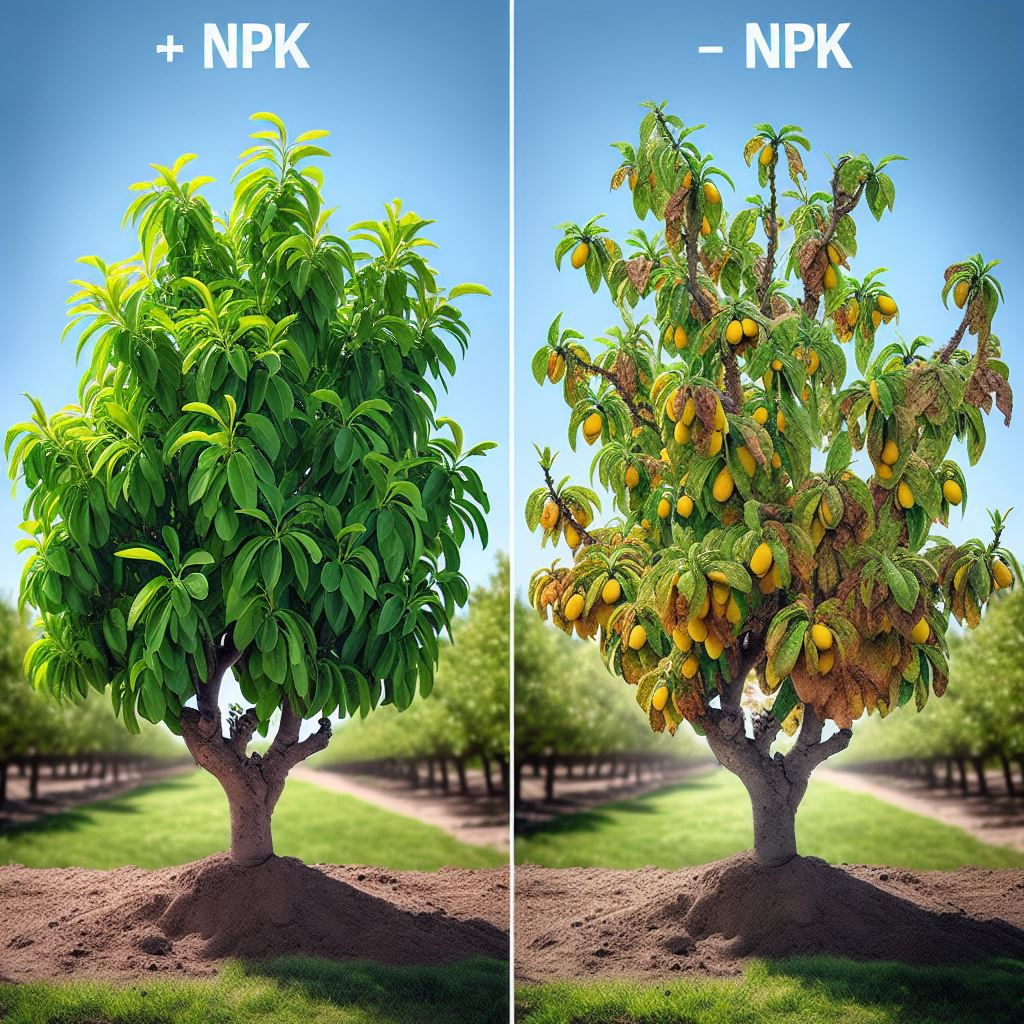
Maximizing almond yield and quality hinges on a comprehensive understanding of nutrient dynamics. Liebig’s Law of the Minimum underscores the criticality of addressing the most limiting nutrient to optimize plant growth. Almond trees, with their biennial growth cycle, necessitate tailored nutrient strategies for vegetative and reproductive phases. A balanced fertilization program, combining fertigation and foliar applications, is crucial for meeting these demands.
Key Nutrient Management Principles
Effective nutrient management in almonds involves:
- Regular soil and tissue testing to monitor nutrient availability and plant status.
- Timely nutrient application aligned with crop phenology to optimize uptake.
- Considering nutrient interactions to prevent imbalances and maximize efficiency.
- Adapting to environmental conditions such as soil type, climate, and irrigation practices.
Precision Nutrient Management
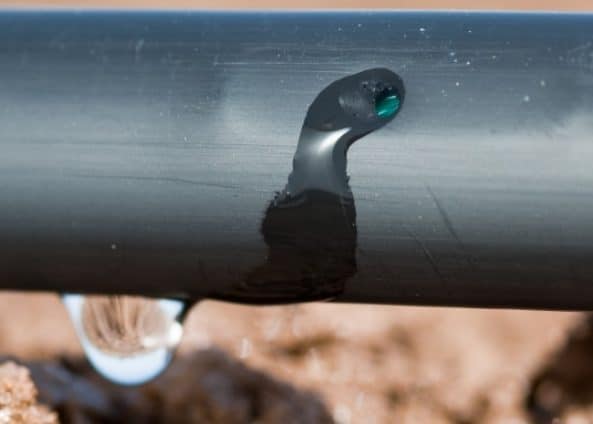
To overcome the limitations of traditional nutrient management approaches, such as the Critical Value method, the development of nutrient demand curves is essential. By correlating nutrient uptake with crop growth stages, we can achieve a more precise and efficient fertilization strategy. Fertigation, when combined with nutrient demand curves, offers the potential to deliver nutrients in a targeted and timely manner.
Challenges and Opportunities
While significant progress has been made in almond nutrient management, several challenges persist. These include
- Accurately determining nutrient requirements under varying environmental conditions.
- Developing cost-effective methods for implementing nutrient demand curves.
- Mitigating the environmental impacts of nutrient management practices.
By addressing these challenges and continuing to invest in research and development, the almond industry can achieve sustainable and profitable production while minimizing its environmental footprint.
Almond Fertilizer Requirements: Precision-Based Nutrient Demand Curves
Understanding the nutrient demand of almond trees is crucial for optimizing growth and maximizing yield. Almond trees require a balanced supply of macronutrients and micronutrients at various growth stages, with each nutrient playing a key role in development, flowering, and fruiting. By timing nutrient applications to coincide with peak demand periods, growers can enhance tree health and productivity while minimizing waste.
Fertilizers are vital for meeting these nutrient needs, ensuring healthy growth and high-quality almonds. Proper timing and application prevent nutrient deficiencies and over-fertilization, reducing environmental impact. For more details on almond fertilizer requirements, see our full article on Almond Fertilizer Requirements.
Nitrogen Management in Almond Orchards
Effective nitrogen management requires a nuanced approach considering various factors.
Key Considerations for Nitrogen Management
- Timing of Application: Nitrogen should be applied when trees are actively growing and require it for nutrient uptake. This typically coincides with bud break and fruit development stages.
- Application Method: Fertigation or foliar sprays can be effective methods for nitrogen application. Fertigation offers better control over nutrient placement and uptake.
- Soil Type and Climate: Soil texture, organic matter content, and local climate conditions influence nitrogen availability and leaching potential.
- Leaf Nitrogen Analysis: Monitoring leaf nitrogen levels can help fine-tune nitrogen applications based on tree needs.
- Environmental Impact: Consider nitrogen leaching and runoff risks to protect water quality.
Nitrogen Management Strategies
Effective management of the almond hull borer requires a combination of tactics:
- Split Applications: Applying nitrogen in multiple smaller doses throughout the growing season can improve efficiency and reduce the risk of nutrient loss.
- Soil Testing: Regular soil analysis helps determine nitrogen availability and informs fertilizer recommendations.
- Cover Crops: Incorporating nitrogen-fixing cover crops can contribute to the orchard’s nitrogen supply.
- Precision Agriculture: Utilizing technologies like variable rate fertilization and soil sensors can optimize nitrogen inputs
Phosphorus (P)
Management Strategies
- Soil Testing: Regularly assess soil phosphorus levels to determine application needs.
- Fertilizer Placement: Apply phosphorus close to the root zone for optimal uptake.
- Consideration of Soil pH: Phosphorus availability is influenced by soil pH.
- Manure Application: Organic sources can provide phosphorus, but availability can be slow.
Potassium (K)
Management Strategies
- Soil Sampling: Analyze soil potassium levels to determine application rates.
- Fertilizer Timing: Apply potassium during periods of high demand, such as fruit growth.
- Leaf Tissue Analysis: Monitor potassium levels in leaves to adjust fertilization as needed.
- Crop Rotation: Consider crops with high potassium requirements in rotation to improve soil potassium levels.
Function and Importance of Macronutrients and Micronutrients in Almond Orchards
Macronutrients and micronutrients are essential for the healthy growth and optimal production of almond trees. Macronutrients like nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K) are required in larger quantities and support vital functions such as leaf and root development, flowering, and nut production. These nutrients are crucial for achieving strong tree growth, maximizing yields, and producing high-quality almonds. On the other hand, micronutrients, including zinc (Zn), boron (B), and iron (Fe), are needed in smaller amounts but are equally important for processes like photosynthesis, pollination, and disease resistance.
Properly managing both macronutrients and micronutrients ensures that almond trees thrive throughout their growing cycle. A well-balanced nutrient program helps prevent deficiencies that can lead to poor growth and reduced yields. For a more detailed understanding of how to manage these nutrients effectively, including their roles at each growth stage, check out our in-depth article on Nutrient Demand and Fertilizer Requirements in Almond Orchards.
Please write 1-2 short paragraphs summarizing the function and importance of macronutrients and micronutrients in almond orchards. The content should provide a concise overview that encourages readers to learn more about this crucial aspect of almond cultivation. The goal is to link this summary to a more in-depth article on the same topic, so the text should be informative yet engaging enough to entice readers to click for further reading.